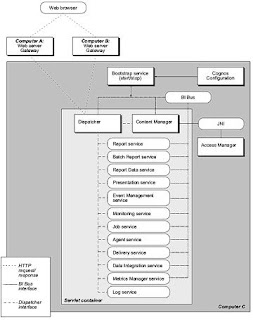
The architecture presented above reflects the Cognos 8 architecture.
Presentation ServiceThe presentation service handles requests for Cognos Connection, Query Studio, and Event Studio.
Report Service
The report service handles interactive requests to run reports and provides output for a user in Cognos Connection or a studio.
Report Data ServiceThe report data service handles requests to import Cognos report data to Microsoft Office workbooks and presentations through Cognos Office Connection.
Batch Report Service
The batch report service handles background requests to run reports and provides output on behalf of the monitoring service.
Job ServiceThe job service runs jobs by signaling the monitoring service to run job steps in the background. Steps include reports, other jobs, import, exports, and so on.
Monitoring ServiceThe monitoring service assigns a target service to handle a scheduled task. For example, the monitoring service may ask the batch report service to run a report, the job service to run a job, or the agent service to run an agent. The monitoring service will monitor the running of the task and collect and save history information for the task. The monitoring service can also take control of asynchronous service conversations on behalf of the client, such as if a user asks to run an interactive report in the background.
Log ServiceThe log service manages all logs generated by the dispatcher and other services. The log service can be configured to record log information in a file, a database, a remote log server, Windows Event Viewer, or a UNIX system log.
Content Manager ServiceThe Content Manager Service performs object manipulation functions in the content store, such as add, query, update, delete, move, and copy.
Metrics Manager Service
The Metrics Manager Service provides the Metric Studio user interface for monitoring and entering performance information.
Data Integration ServiceThe data integration service controls the loading of metrics data and the calculation of metrics status for scorecarding in Metric Studio.
Delivery ServiceThe delivery service sends emails on behalf of other services, such as the report service, job service, agent service, or data integration service.
Event Management ServiceThe event management service manages scheduled tasks. When a scheduled task begins to run, the event management service asks the monitoring service to begin running the task.
Agent ServiceThe agent service runs agents. If the conditions for an agent are met when the agent runs, the agent service asks the monitoring service to run the tasks.
System ServiceThe system service defines the Business Intelligence Bus API-compliant service used to obtain application-wide Cognos 8 configuration parameters. It also provides methods that normalize and validate locale strings and map locale strings to locales supported by the application.
LDAP Authentication Integration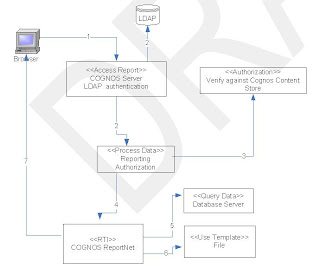
Reporting client connects to Reporting server directly. Reporting server does user authentication first (LDAP binding). After authentication is passed, Cognos Content Store authorization applies; Available reports are displayed as a list. Different user groups have different report group access. The diagram describes processes for all user groups.
Messaging and Dispatching in the Reporting LayerIn the reporting layer, messaging occurs between the gateway, the dispatcher, and the content manager. Requests can have different levels of affinity. Affinity refers to whether a request is assigned to a specific server or whether a load-balancing mechanism can assign it to another server. Affinity between request and server ensures that requests are routed to an appropriate computer for processing. There are three types of affinity: absolute, high, and low. The cancel operation is handled with a dedicated connection and does not have an affinity type. Details regarding affinity and load balancing can be found in the ‘Cognos 8 Business Intelligence Architecture and Planning Guide’. The following extract provides and overview as well as a sample explanation on processing a report execution request.
Absolute Affinity
Absolute (control) affinity requests are always routed back to the server that processed the original request. For example, when a user cancels a running report, absolute affinity routes the cancel request back to the executing process. Absolute affinity is used to create an association between the client and the executing server to ensure that long-running requests do not time out.
Cognos 8 routes absolute affinity requests to a specific server, regardless of the load balancing used. An absolute affinity request is used with the following operations: wait, getOutput, and release.
High Affinity
High affinity requests can be processed on any of a number of servers, but resource consumption is minimized if the request is routed back to the executing process.
For example, when a pageDown command is run while reading a report, the command can be run most efficiently by using the process that served up the page that is shown. If that process is not available because the administrator shut down the computer or there was a network failure, the request is routed to another available process. The next page can still be served up, although the process will be slower.
Cognos 8 routes high affinity requests to a specific server regardless of the load balancing used. A high affinity request is used with the following operations: back, email, firstPage, forward, lastPage, nextPage, previousPage, print, render, save, and saveAs.
Low Affinity
Low affinity requests will operate just as efficiently on any computer.
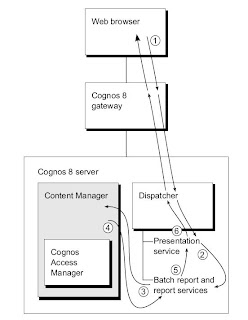
When a user runs an HTML report or analysis through Cognos Connection, the following occurs:
1. The user clicks a report or analysis to run it, and the request goes through the gateway and the dispatcher to the presentation service.
2. The presentation service sends the request to the report service through the dispatcher.
3. The report service requests the report or analysis and metadata from Content Manager, through the dispatcher.
4. Content Manager sends the report or analysis XML specifications and metadata to the report service. Content Manager refetches metadata only when Cognos 8 is stopped and restarted or the model is updated and republished.
5. The report service returns one of these results to the presentation service:
- • an error page
- • a not ready page
- • a page of an HTML report or analysis
6. The presentation service sends one of these results through the dispatcher and gateway to the browser:
- • an error page
- • a wait or cancel page
- • a page of a completed HTML report or analysis in the Cognos Viewer interface
When the user presses page down or page bottom in the browser, the same path is followed again. The request has a high state of request affinity to ensure that it is routed to the same report service for additional rows of data
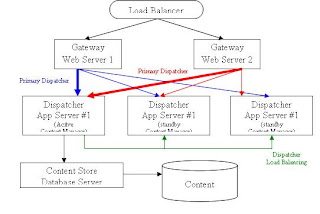
Load BalancingThe Cognos 8 architecture is tuned to minimize dispatch time. Cognos 8 uses network capabilities such as load-balancing routers to ensure that dispatchers and Web gateways are evenly utilized. Load balancing routers 'spray' requests across multiple Web or application servers. Although each Cognos 8 application servers has a Content Manager installed, only one is active and the other(s) are in a ‘standby’ status. Since application servers in ‘standby’ mode have more computer resource available to service report request, load balancing settings will be adjusted to direct more request to ‘standby’ servers in an effort to maintain an overall balance of resource utilization across the servers.
Gateways may be configured to recognize multiple dispatchers, however the first dispatcher listed is the primary and will be sent all request unless there is a failure. Consequently, this feature supports failover functionality but not actual load balancing.
The dispatchers are also able to balance service requests across dispatchers sharing the same content store. The dispatcher load balancing scheme is a static algorithm. A weight for each machine can be specified; a dispatcher with a weight of 2 can do twice as much work as a dispatcher with a weight of 1, and so on. Each dispatcher then simply spreads work among all the dispatchers using a weighted round-robin algorithm. Each dispatcher will accept all requests passed its way. Requests are queued by the dispatcher until executed
Load balancing is automatic in a distributed install. If there is more than one instance of a report service, dispatcher will distribute requests to all enabled instances of the service that are registered in Content Manager. The configured server Capacity determines the relative weights of the servers. Over time, a dispatcher with a capacity of 2.0 will receive twice as many requests as a dispatcher with a capacity of 1.0. In addition, Cognos 8 supports load-balancing routers.
If load-balancing routers or equivalent network technology is not used, browser requests are directed to a single Web server, as indicated in the URL. Similarly, Cognos 8 Web gateway requests are directed to a single Cognos Cognos 8 server.
Load-balancing routers and other network technologies are used to distribute network requests across several computers to ensure an even allocation of work. Load-balancing routers can be used with Cognos 8 in front of the web servers and the applications servers. The recommendation is to use them before the web servers and use the load balancing features of the dispatchers to balance the load across the dispatchers.
- Between the Client Tier: web browser or Framework Manager and Web Tier : Web Server Gateway
- Between Web Tier: Web Server Gateway and Application Tier: Report Server
Note: To ensure that requests are managed efficiently, some requests are routed back to the same report server. Cognos 8 does this automatically. The use of one or more load-balancing routers will not disrupt this process.
Cognos 8 Java Servlets and ServicesCognos 8 operates as two Java servlets running in a J2EE-compliant servlet container. The first servlet is the dispatcher. The presentation service, and the job and schedule monitoring service, are Java based and run within the dispatcher. The report service is a non-Java based application running as a child process of the dispatcher.
The second Java servlet is Content Manager, which runs in the same Java process as the dispatcher.
The main incoming port (by default 9300) is owned and managed by the servlet container or application server that routes messages to the appropriate servlet based on the URL.
Multi-Thread ManagementThe J2EE servlet container manages the threads (computing instructions) for each user request. This varies from a traditional C++ based application, where threads are managed by the service itself.
The Java servlet architecture provides a key advantage. If a failure occurs, only the thread associated with the request is affected. The failure does not impact the service as a whole. In other words, the affected thread will be lost, but other requests will be unaffected, and the system will continue to operate.
In addition, each report server creates and manages own threads. The report server is started and monitored by the dispatcher. If the report server fails, the dispatcher will start a new report server. The affected threads will be lost, but the system will continue to process new requests
Database Connection ManagementContent Store DatabaseThe Content Manager Service accesses the content store. Content Manager uses one database connection per request. Content Manager creates new database connections as required, pools connections, and re-uses existing connections when possible. Content Manager maintains all database connections for the duration of the Content Manager operation. The theoretical maximum number of concurrent Content Manager Requests is equal to the number of requests accepted by the Java application server.
When other Cognos 8 services are on the same computer as Content Manager, requests may be divided between Content Manager and the other services. In this case, the number of connections available to Content Manager may be less than the maximum possible connections.
The diagram below shows the use of JDBC for internal managed Cognos databases and the use of native API for reporting data sources.
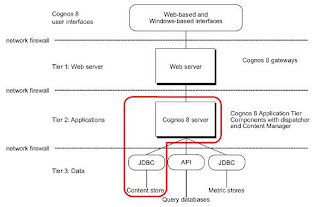
The report server computer accesses the query databases. The maximum number of query database connections available can be configured to the report server computer, and the amount of time connections are retained. A cleanup thread examines the connections once per minute and any connection that has been inactive longer than the timeout value is removed.
Inactive query database connections can be claimed by a new request. This occurs when the maximum number of connections has been reached and none of the inactive connections can be used by the new request. In this case the oldest inactive connection is terminated and a new connection is created. A query database connection is only reused when the database credentials of the connection match those of the new request. When the maximum number of connections is reached, and all are active, then additional requests fail.